..................................................................................................................................................................................................................

..................................................................................................................................................................................................................


EMF stands for electromagnetic fields. Radio waves are one form of EMF. So is ordinary light. Electromagnetic fields are produced by every electrical or electronic device. This includes electrical wiring and power lines, computers, televisions, wireless devices such as cell phones and WiFi devices, microwave ovens, all forms of broadcasting including AM, FM, and TV, etc. Visible light as well as invisible forms such as infrared, and ultraviolet, X-Rays, and gamma rays are also forms of EMF.
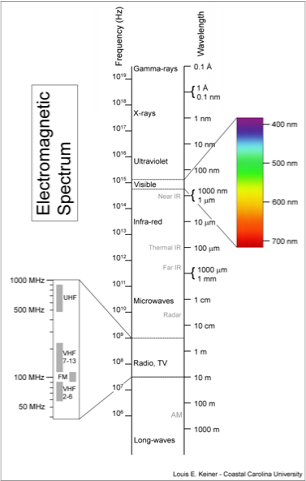
All these different forms of EMF are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Electromagnetic waves cover a vast frequency range from ELF Extremely low frequency of less than 1 Hz (cycles per second) up to hard gamma rays at over 300 EHz (EHz is 10 to the power 18 cycles per second). See Figure 1 for a picture of the electromagnetic spectrum. Every EMF frequency is also associated with a wavelength and an inherent level of quantum energy. The quantum energy is the energy of the individual light particles known as photons. Low frequencies have long wavelengths and low photon energy. Higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths and higher photon energy. See the table in Figure 2 for a summary of these relationships. Please also see the following excellent article on Electromagnetic radiation on the Wikipedia Encyclopedia web site.
There are only three scientifically established mechanisms where EMF is known to cause health effects. The relative importance of these mechanisms depends on frequency and is also strength and/or power dependent. The three mechanisms are the following: induced voltage gradients and/or electric currents in the body, thermal effects, and ionizing radiation effects. Extensive scientific testing has been used to measure these effects and to establish safe limits.
Induced voltage gradients and/or electric currents in the body are the only known health effects in the presence of strong electric and magnetic fields at low frequencies in the range of 0 - 3 KHz. Safety limits for this class of effects have been established by the IEEE (IEEE Standard C95.6). These limits are established to stay below the excitation thresholds of various tissues. Excessive excitation may result in electrical shock and/or burns. RF shock and burns are also possible at frequencies up to 30 MHz. The safe limits for electric and magnetic fields are set by the IEEE and FCC and other public health bodies according to frequency.
Thermal effects are the primary health effects when living tissue absorbs enough EMF power to cause heating. This effect is the primary concern in the RF frequency range of 30 MHz to 300 GHz. Harmful effects from induced voltages and currents may still occur, but at power levels above those for heating effects. In theory, the total EMF power absorbed by tissue is determined by the photon energy multiplied by the number of photons per second being absorbed. But in practice, the method utilized is based on the measurement of the Specific Absorption Rate or SAR. The SAR safety limits are specified in units of W/kg of body tissue. This heating effect is the principle that microwave ovens are based on. Existing regulations from entities such as the FCC in the US, the WHO, and the ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation) have set safety limits for all commercial products that are well below the level where harmful heating effects may occur. For example in the FCC OET Bulletin 56, the level for "whole body" exposure for the general public is set at a level that is 50 times lower than the level at which harmful heating occur (see footnotes on P 13 of this FCC document).
EMF can also cause harm when its inherent photon energy reaches the level where it can break the electron bonds that hold molecules together. This is termed ionizing radiation, and it is an entirely different mechanism than the heating effect. Fig 3 shows that EMF becomes ionizing at short ultraviolet wavelengths. This is what causes sunburn, which can also increase the risk of skin cancer. Ionizing radiation can cause many other types of cancer. X-rays and gamma rays have even shorter wavelengths and higher photon energy and are considered the most dangerous forms of ionizing radiation. The energy level of the photons produced by cell phones is more than 10 million times below that of the lowest energy ultraviolet ionizing radiation (See Fig. 3).
Research is ongoing on the effects of EMF on health. These investigations cover all forms of EMF ranging from power line frequencies and up through microwaves. Various forms of investigation have been and are being carried out. These include epidemiological, in vitro (cell cultures) and in vivo (animal) studies. No clear and consistent evidence for harmful health effects has been found other than the ones described. For example, in cases where some evidence for harm has been found, higher quality follow up studies have failed to find any effect. The SCENIHR Committee of the European Commission has just released (Jan 2009) an excellent 86 page report as well as a summary for the public on the current state of scientific research. A link to these reports is provided on the Evidence Based Science Web Sites page.
All these different forms of EMF are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Electromagnetic waves cover a vast frequency range from ELF Extremely low frequency of less than 1 Hz (cycles per second) up to hard gamma rays at over 300 EHz (EHz is 10 to the power 18 cycles per second). See Figure 1 for a picture of the electromagnetic spectrum. Every EMF frequency is also associated with a wavelength and an inherent level of quantum energy. The quantum energy is the energy of the individual light particles known as photons. Low frequencies have long wavelengths and low photon energy. Higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths and higher photon energy. See the table in Figure 2 for a summary of these relationships. Please also see the following excellent article on Electromagnetic radiation on the Wikipedia Encyclopedia web site.
There are only three scientifically established mechanisms where EMF is known to cause health effects. The relative importance of these mechanisms depends on frequency and is also strength and/or power dependent. The three mechanisms are the following: induced voltage gradients and/or electric currents in the body, thermal effects, and ionizing radiation effects. Extensive scientific testing has been used to measure these effects and to establish safe limits.
Induced voltage gradients and/or electric currents in the body are the only known health effects in the presence of strong electric and magnetic fields at low frequencies in the range of 0 - 3 KHz. Safety limits for this class of effects have been established by the IEEE (IEEE Standard C95.6). These limits are established to stay below the excitation thresholds of various tissues. Excessive excitation may result in electrical shock and/or burns. RF shock and burns are also possible at frequencies up to 30 MHz. The safe limits for electric and magnetic fields are set by the IEEE and FCC and other public health bodies according to frequency.
Thermal effects are the primary health effects when living tissue absorbs enough EMF power to cause heating. This effect is the primary concern in the RF frequency range of 30 MHz to 300 GHz. Harmful effects from induced voltages and currents may still occur, but at power levels above those for heating effects. In theory, the total EMF power absorbed by tissue is determined by the photon energy multiplied by the number of photons per second being absorbed. But in practice, the method utilized is based on the measurement of the Specific Absorption Rate or SAR. The SAR safety limits are specified in units of W/kg of body tissue. This heating effect is the principle that microwave ovens are based on. Existing regulations from entities such as the FCC in the US, the WHO, and the ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation) have set safety limits for all commercial products that are well below the level where harmful heating effects may occur. For example in the FCC OET Bulletin 56, the level for "whole body" exposure for the general public is set at a level that is 50 times lower than the level at which harmful heating occur (see footnotes on P 13 of this FCC document).
EMF can also cause harm when its inherent photon energy reaches the level where it can break the electron bonds that hold molecules together. This is termed ionizing radiation, and it is an entirely different mechanism than the heating effect. Fig 3 shows that EMF becomes ionizing at short ultraviolet wavelengths. This is what causes sunburn, which can also increase the risk of skin cancer. Ionizing radiation can cause many other types of cancer. X-rays and gamma rays have even shorter wavelengths and higher photon energy and are considered the most dangerous forms of ionizing radiation. The energy level of the photons produced by cell phones is more than 10 million times below that of the lowest energy ultraviolet ionizing radiation (See Fig. 3).
Research is ongoing on the effects of EMF on health. These investigations cover all forms of EMF ranging from power line frequencies and up through microwaves. Various forms of investigation have been and are being carried out. These include epidemiological, in vitro (cell cultures) and in vivo (animal) studies. No clear and consistent evidence for harmful health effects has been found other than the ones described. For example, in cases where some evidence for harm has been found, higher quality follow up studies have failed to find any effect. The SCENIHR Committee of the European Commission has just released (Jan 2009) an excellent 86 page report as well as a summary for the public on the current state of scientific research. A link to these reports is provided on the Evidence Based Science Web Sites page.
Fig 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum

Fig 2 Frequency vs Wavelength vs Energy
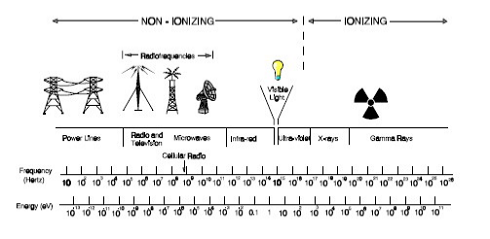
Fig 3 EMF Non-Ionizing & Ionizing Radiation (from FCC OET Bulletin 56)

Except where noted all images on this web site are taken from the Wikipedia commons
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners Copyright 2009 EMF & Health
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners Copyright 2009 EMF & Health